One thousand firefighters are in the back yard of the American Indian College Fund headquarters, battling Colorado’s third largest forest fire in history, dubbed the High Park Fire. And there’s a good chance that several firefighters are American Indians, thanks to Salish Kootenai College’s firefighting program in Pablo, Montana.
The nearly 50,000-acre fire, which was started by lightning and was reported Saturday, is fast-moving because it is feeding on dead trees left behind due to bark beetle infestation, and was fanned by winds and dry and hot conditions. Flames have crowned as high as 30 feet and some have stretched sideways due to winds on Monday.
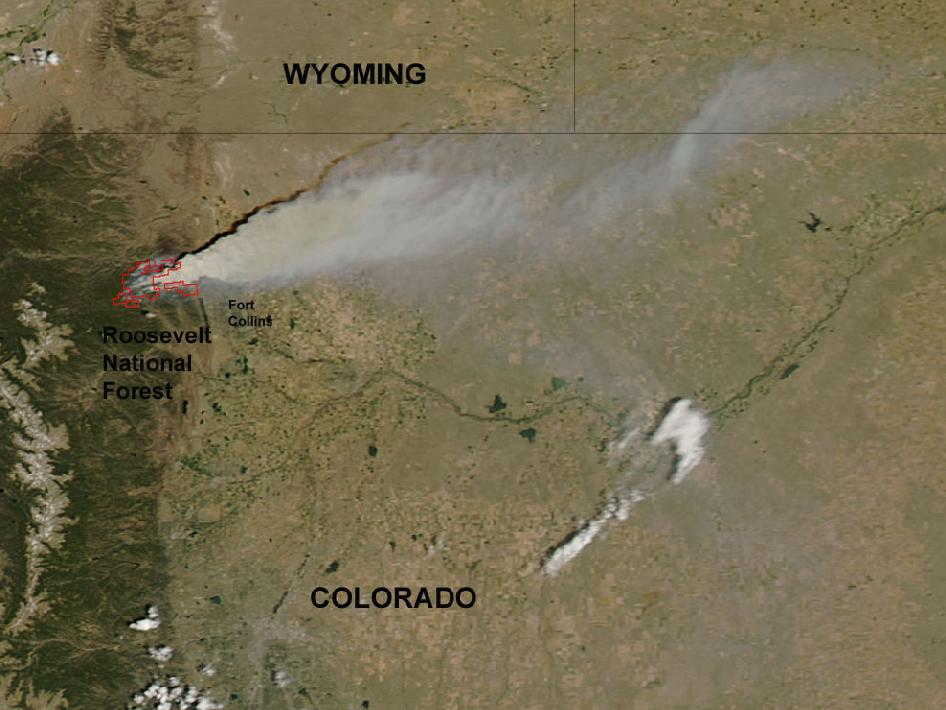
NASA Satellite Imagery of Colorado’s High Park Fire
To battle this fierce foe, firefighters use old techniques combined with modern technology. These tactics are learned by students studying Natural Resources and Conservation at Salish, where the curriculum prepares individuals in forest fire-fighting techniques along with other forestry and natural resources subjects.
The tribes of the Flathead Indian Reservation, home to Salish Kootenai College, have developed a large and sophisticated tribal government that includes a Natural Resources Department recognized as among the most accomplished in the U.S. The department marries technical prowess with the tribes’ traditional cultural values and wisdom of the earliest practitioners of conservation biology in the Flathead Watershed, which is rooted in generations of observations and interactions with the natural world. The Natural Resources Department oversees the Forestry Department, which manages forestry and fire programs. Salish Kootenai College ensures that tribal members are educated and trained for their roles to preserve and protect natural resources, including fighting fires, in Montana and across the nation.
How do firefighters fight forest fires?
The attack plan in Colorado is to combine traditional firefighting methods which date to a 1910 forest fire that devoured 3 million acres in Salish’s back yard in Montana, as well as neighboring Washington and Idaho, with a high-tech air assault.
Firefighters on the ground are using picks and axes, hacking barriers into the dirt inch by inch, and lighting back fires. At last count, 250 aircraft are fighting the fire from the sky. Aided by satellite imagery, helicopters are sucking up water from a nearby reservoir using long hoses and dropping it onto the inferno and areas where they are trying to prevent burning. Air tankers are dousing areas with chemical retardant.
Command centers on the ground are marshaling forces forward in a continuous line, establishing anchor points and using natural barriers like roads, creeks or cliffs, so the fire can’t double back and trap firefighters in the blaze.
The goal of firefighters is to contain or control the fire until it burns itself out, not to eliminate it. They construct a fire line constructed that goes all the way down to the mineral soil where the fire can’t burn, and heavy burning fuels mopped up or 100 feet away from the line created by ground crews. Doing this keeps the area of the burn under the watchful eye of fire crews and away from communities, dwellings and other structures, where it could be a danger to people.
The American Indian College Fund is thankful to and proud of all of our firefighters that are working hard to preserve our communities and forests from devastation, and we want to especially thank our Native firefighters for their sacrifice.









